
President-Elect Donald Trump has announced significant tariff increases on imports from Canada, Mexico, and China as part of his administration’s efforts to address issues related to drugs and illegal immigration.
25% Tariff on Imports from Canada and Mexico
On January 20, President-Elect Trump will implement a 25% tariff on all products imported from Canada and Mexico. This decision is driven by concerns over the influx of illegal immigration and drug trafficking, particularly the flow of fentanyl, which has been linked to approximately 100,000 deaths annually in the U.S.
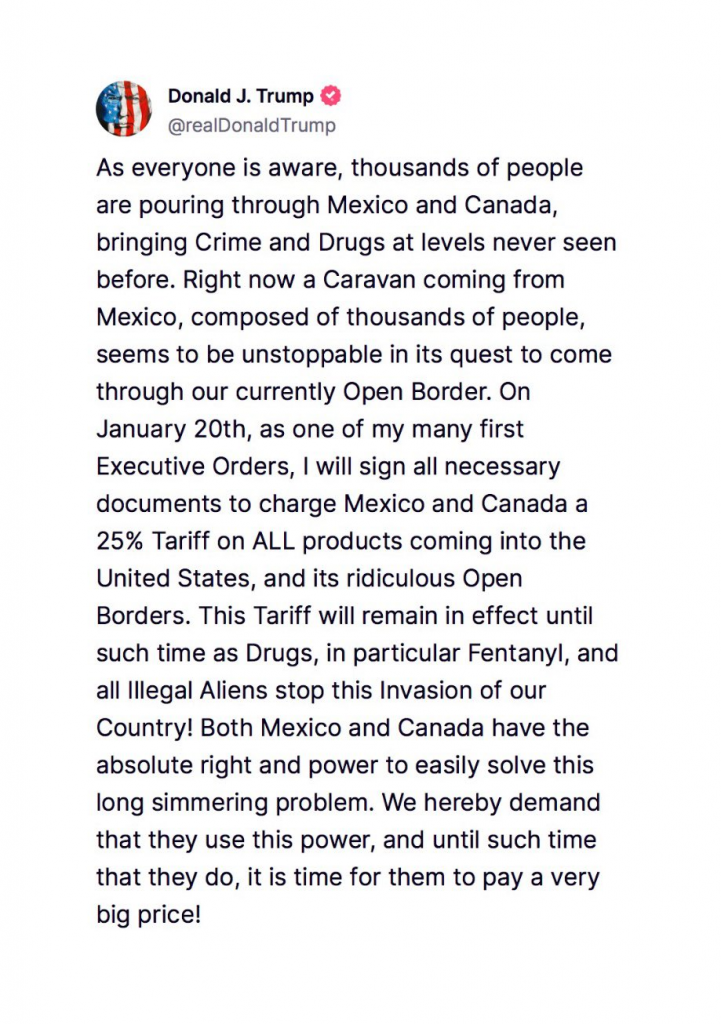
The tariff will remain in effect until both countries effectively address these issues. Trump emphasized, “Mexico and Canada have the absolute right and power to easily solve this long-simmering problem,” indicating his expectation for these nations to take immediate action against drug trafficking and illegal migration.
This tariff is positioned as a response to the ongoing challenges posed by illegal border crossings that are perceived to be exacerbated by open border policies. The implementation of this tariff marks a significant shift in trade relations with neighboring countries and aims to compel them to take greater responsibility for border security and drug enforcement.
10% Additional Tariff on Chinese Imports
In conjunction with tariffs on Canada and Mexico, Trump has also announced an additional 10% tariff on Chinese imports. This measure specifically targets the ongoing issue of drug trafficking, particularly fentanyl, which is reportedly being sent into the U.S. from China, often through routes established in Mexico.
Trump stated, “Until such time as they stop, we will be charging China an additional 10% tariff… on all of their many products coming into the United States.” This announcement follows previous discussions with Chinese representatives regarding their commitment to curb drug exports, which have not yielded satisfactory results thus far.
The backdrop to this tariff increase includes findings from a U.S. House Select Committee report indicating that the Chinese regime has played a role in facilitating the proliferation of fentanyl in the U.S. The anticipated impact of these tariffs includes potential inflationary pressures in the U.S. economy, as higher import costs could translate to increased prices for consumers.
Immediate Macroeconomic Implications
The announcement of these tariffs has already had observable effects on financial markets. Following Trump’s declaration, the U.S. dollar experienced a surge, recovering from losses related to recent market reactions to the appointment of Scott Bessent as Treasury Secretary.
Meanwhile, both the Mexican peso and Canadian loonie saw declines against the dollar, and the offshore yuan was also negatively impacted. Analysts suggest that this response may reflect a market realization of the potential economic shifts stemming from these trade measures.
Goldman Sachs analysts have noted that the market’s reaction to the tariff announcements may be somewhat exaggerated. They indicated that the less aggressive approach regarding tariffs compared to previous expectations, along with the layered rollout of tariffs, might mitigate some of the anticipated economic disruption.
Their projections suggest that additional U.S. tariffs on Chinese goods could reach 20% by 2025, with a predicted rise in the USD/CNY exchange rate to 7.4-7.5 in the next three to six months.
Broader Market Reactions and Future Considerations
U.S. futures showed modest gains following the announcement, but stock markets in Japan, Australia, and South Korea dropped. Market analysts are observing these developments closely, particularly given the potential for ongoing negotiations between the U.S. and China, which may be influenced by future concessions from China concerning issues such as human rights and market access.
Industry leaders have expressed concerns that Trump’s tariff increases could lead to significant economic consequences, particularly for Hong Kong manufacturers, who may be compelled to seek alternative markets in Southeast Asia and the Middle East.
The impact on exports from Hong Kong and China is expected to be severe, affecting local economies reliant on trade with the U.S. Economists predict that Trump’s tariff measures could not only hinder export levels but also exacerbate domestic inflation in the U.S. as imported goods become pricier.
Gary Ng Cheuk-yan from Natixis remarked that the proposed tariff increase, while lower than previous threats, signals a potential continuation of punitive trade measures against China. He urged mainland and Hong Kong manufacturers to prepare for the economic fallout by relocating supply chains to mitigate the effects of increased duties.
In conclusion, the combined tariff increases on Canada, Mexico, and China represent a significant shift in U.S. trade policy with potential wide-ranging implications for global trade, currency valuations, and domestic economic conditions.
As these tariffs are set to take effect, the economic landscape is likely to undergo further changes, demanding close monitoring by stakeholders in affected markets.
Disclaimer: All information provided on this website is for informational purposes only and should not be construed as financial or investment advice. We do not guarantee the accuracy, completeness, or timeliness of the information, and we are not responsible for any financial decisions you may make based on this information. Cryptocurrencies are highly volatile assets, and any investment in them carries a high level of risk.
More Like This

US Manufacturing PMI Rises to 49.7 in November

PCE Inflation Comes In-Line With Expectations
*AI technology may have been used to develop this story and publish it as quickly as possible.

